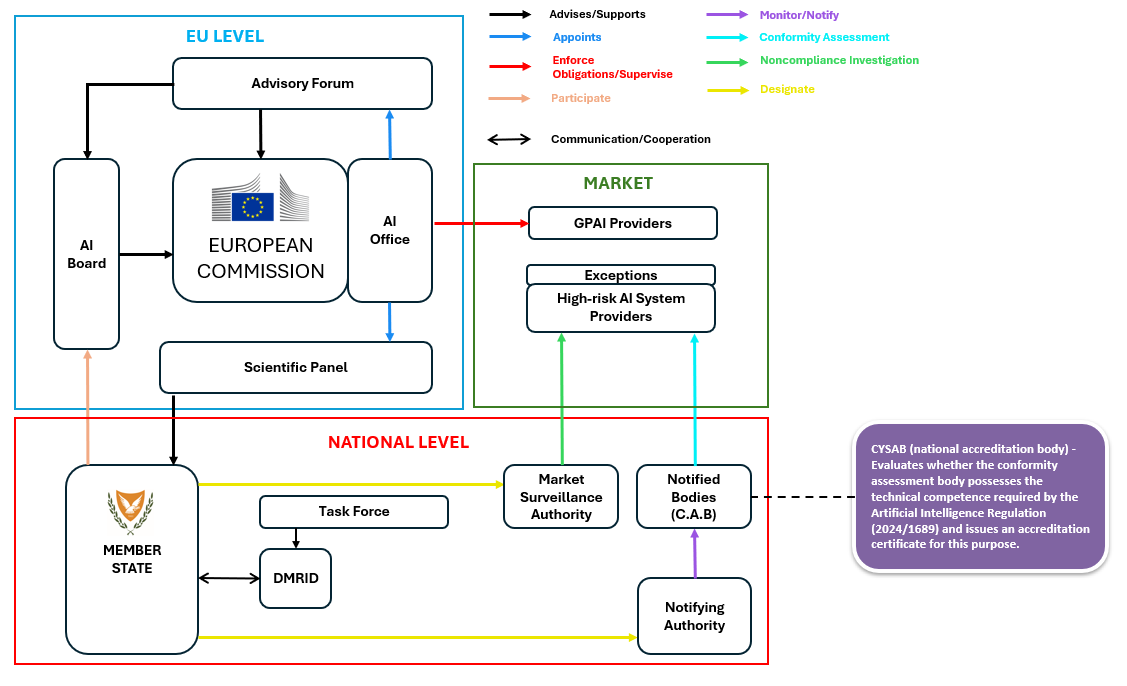
Reception & Assessment Responsibilities:
- Application Review: Receive and assess applications for notification from conformity assessment bodies.
- Documentation Review: Assess relevant documentation for designation, notification, and monitoring (Arts. 29–39).
- Assess documentation related to subcontractors or subsidiaries, retaining it for 5 years post-subcontract.
- Assess information provided by notified bodies under Article 45(1).
- Commission Requests: Provide the Commission with relevant information upon request regarding notifications or the competence of notified bodies.
Notification Responsibilities:
Notify Conformity Bodies:
- Only notify bodies that meet the requirements of Article 31. Use the electronic notification tool to inform the Commission and Member States of notifications.
- Update Notifications: Notify the Commission and Member States of any relevant changes to a notified body’s status.
Suspension, Restriction & Withdrawal:
Oversight of Notified Bodies:
- Monitor notified bodies for continued compliance with Article 31.
- Investigate if there’s reason to believe a body no longer meets the requirements or fails in obligations.
Take Action:
- Ιf non-compliance is found, restrict, suspend, or withdraw the designation as appropriate.
- Assess the impact on issued certificates.
- Require suspension of affected certificates and inform the Commission and Member States.
Commission Findings:
Assess and act on Commission findings regarding non-compliant notified bodies.
Reporting & Communication:
Reporting Failures: Submit a report to the Commission and Member States when a designation is affected.
Other Member States' Objections: Allow for objections by other Member States under Article 30(4) and (5).
Coordination & Participation:
Group Participation: Ensure notified bodies participate in the group referred to in Article 38(1), directly or via representatives.